特别说明:该专栏文章均来源自微信公众号《大数据实战演练》,欢迎关注!
前言
最近工作中需要实现HBase自定义扩展sms4加密,今天就先来说一下Java版的SMS4加密解密算法的具体实现。
一、概述
1.1 基本概念
本算法是一个分组算法,由加解密算法和密钥扩展算法组成。该算法的分组长度为128比特(Bit),密钥长度为128比特(Bit),也就是16个字节(Bytes)。加密算法与密钥扩展算法都采用32轮非线性迭代结构。解密算法与加密算法的结构相同,只是轮密钥的使用顺序相反,解密轮密钥是加密轮密钥的逆序。在SMS4的基础类中,你会看到加密和解密的基础函数是同一个(本篇文章中的sms4KeyExt()方法),只是需要一个int型的标志位来判断是加密还是解密。
1.2 密码算法结构
基本轮函数加迭代解密算法与加密算法相同1.3 S盒:S-box
S 盒为固定的8比特(Bit)输入8比特(Bit)输出的置换,记为Sbox(⋅) 。
1.4 SMS4密码算法
1.4.1 基本运算
⨁ 32比特异或⋘ i 32比特循环左移i位1.4.2 基本密码部件
非线性字节变换部件S盒非线性字变换τ:32位字的非线性变换字线性部件L变换字合成变换T1.4.3 轮函数F
1.5 密钥扩展算法
常数FK固定参数CK更多详细的资料请私信 “sms4” 到本头条号,获取SMS4相关资料(一个PPT,一个PDF)。
二、编码实现
以下代码可能与网上有些雷同,毕竟万变不离其宗,但我将每一个方法代表什么意思,都写了很详细的注释供大家理解,这样可以缩短你的学习时长。都快被自己感动哭了
package com.xxx.sms4;\nimport java.util.Arrays;\n/**\n * @author CREATE_17\n * @description: SMS4加密与解密算法实现\n * @date: 2019/4/2 14:10\n */\npublic class Sms4 {\n /**\n * @description: ENCRYPT与DECRYPT为加解密的判断依据\n */\n private static final int ENCRYPT = 1;\n private static final int DECRYPT = 0;\n /**\n * @description: 轮数,轮函数的迭代次数\n * 加密算法与密钥扩展算法都采用32轮非线性迭代结构。\n */\n private static final int ROUND = 32;\n private static final int BLOCK = 16;\n /**\n * @description: S盒中数据均采用16进制表示\n */\n private static short[] sBox = {\n 0xd6, 0x90, 0xe9, 0xfe, 0xcc, 0xe1, 0x3d, 0xb7, 0x16, 0xb6, 0x14, 0xc2, 0x28, 0xfb, 0x2c, 0x05,\n 0x2b, 0x67, 0x9a, 0x76, 0x2a, 0xbe, 0x04, 0xc3, 0xaa, 0x44, 0x13, 0x26, 0x49, 0x86, 0x06, 0x99,\n 0x9c, 0x42, 0x50, 0xf4, 0x91, 0xef, 0x98, 0x7a, 0x33, 0x54, 0x0b, 0x43, 0xed, 0xcf, 0xac, 0x62,\n 0xe4, 0xb3, 0x1c, 0xa9, 0xc9, 0x08, 0xe8, 0x95, 0x80, 0xdf, 0x94, 0xfa, 0x75, 0x8f, 0x3f, 0xa6,\n 0x47, 0x07, 0xa7, 0xfc, 0xf3, 0x73, 0x17, 0xba, 0x83, 0x59, 0x3c, 0x19, 0xe6, 0x85, 0x4f, 0xa8,\n 0x68, 0x6b, 0x81, 0xb2, 0x71, 0x64, 0xda, 0x8b, 0xf8, 0xeb, 0x0f, 0x4b, 0x70, 0x56, 0x9d, 0x35,\n 0x1e, 0x24, 0x0e, 0x5e, 0x63, 0x58, 0xd1, 0xa2, 0x25, 0x22, 0x7c, 0x3b, 0x01, 0x21, 0x78, 0x87,\n 0xd4, 0x00, 0x46, 0x57, 0x9f, 0xd3, 0x27, 0x52, 0x4c, 0x36, 0x02, 0xe7, 0xa0, 0xc4, 0xc8, 0x9e,\n 0xea, 0xbf, 0x8a, 0xd2, 0x40, 0xc7, 0x38, 0xb5, 0xa3, 0xf7, 0xf2, 0xce, 0xf9, 0x61, 0x15, 0xa1,\n 0xe0, 0xae, 0x5d, 0xa4, 0x9b, 0x34, 0x1a, 0x55, 0xad, 0x93, 0x32, 0x30, 0xf5, 0x8c, 0xb1, 0xe3,\n 0x1d, 0xf6, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x82, 0x66, 0xca, 0x60, 0xc0, 0x29, 0x23, 0xab, 0x0d, 0x53, 0x4e, 0x6f,\n 0xd5, 0xdb, 0x37, 0x45, 0xde, 0xfd, 0x8e, 0x2f, 0x03, 0xff, 0x6a, 0x72, 0x6d, 0x6c, 0x5b, 0x51,\n 0x8d, 0x1b, 0xaf, 0x92, 0xbb, 0xdd, 0xbc, 0x7f, 0x11, 0xd9, 0x5c, 0x41, 0x1f, 0x10, 0x5a, 0xd8,\n 0x0a, 0xc1, 0x31, 0x88, 0xa5, 0xcd, 0x7b, 0xbd, 0x2d, 0x74, 0xd0, 0x12, 0xb8, 0xe5, 0xb4, 0xb0,\n 0x89, 0x69, 0x97, 0x4a, 0x0c, 0x96, 0x77, 0x7e, 0x65, 0xb9, 0xf1, 0x09, 0xc5, 0x6e, 0xc6, 0x84,\n 0x18, 0xf0, 0x7d, 0xec, 0x3a, 0xdc, 0x4d, 0x20, 0x79, 0xee, 0x5f, 0x3e, 0xd7, 0xcb, 0x39, 0x48\n };\n /**\n * @description: 常数FK,在密钥扩展中使用一些常数\n */\n private static int[] fk = {0xa3b1bac6, 0x56aa3350, 0x677d9197, 0xb27022dc};\n /**\n * @description: 32个固定参数CK\n * 产生规则:Ckij= (4i+j)×7(mod 256) ,i=0,1,2…31,j=0,1,…3\n */\n private static int[] ck = {\n 0x00070e15, 0x1c232a31, 0x383f464d, 0x545b6269,\n 0x70777e85, 0x8c939aa1, 0xa8afb6bd, 0xc4cbd2d9,\n 0xe0e7eef5, 0xfc030a11, 0x181f262d, 0x343b4249,\n 0x50575e65, 0x6c737a81, 0x888f969d, 0xa4abb2b9,\n 0xc0c7ced5, 0xdce3eaf1, 0xf8ff060d, 0x141b2229,\n 0x30373e45, 0x4c535a61, 0x686f767d, 0x848b9299,\n 0xa0a7aeb5, 0xbcc3cad1, 0xd8dfe6ed, 0xf4fb0209,\n 0x10171e25, 0x2c333a41, 0x484f565d, 0x646b7279\n };\n /**\n * @description: 移位,rot1(x,y)为循环左移位y\n * @param: x\n * @param: y\n * @return: int\n */\n private int rotl(int x, int y) {\n return x << y | x >>> (32 - y);\n }\n /**\n * @description: 加解密,非线性τ函数:B=τ(A)\n * @param: a\n * @return: int\n */\n private int byteSub(int a) {\n return (sBox[a >>> 24 & 0xFF] & 0xFF) << 24\n ^ (sBox[a >>> 16 & 0xFF] & 0xFF) << 16\n ^ (sBox[a >>> 8 & 0xFF] & 0xFF) << 8\n ^ (sBox[a & 0xFF] & 0xFF);\n }\n /**\n * @description: 加解密的L函数\n * @param: b\n * @return: int\n */\n private int l1(int b) {\n return b ^ rotl(b, 2) ^ rotl(b, 10) ^ rotl(b, 18) ^ rotl(b, 24);\n }\n /**\n * @description: 密钥扩展\n * @param: b\n * @return: int\n */\n private int l2(int b) {\n return b ^ rotl(b, 13) ^ rotl(b, 23);\n }\n /**\n * @description: SMS4的加密方法实现\n * @param: input(待输入的明文)\n * @param: output(待输出的密文)\n * @param: rk(轮密钥)\n * @return: void\n */\n private void sms4Crypt(byte[] input, byte[] output, int[] rk) {\n int mid;\n int[] x = new int[4];\n int[] tmp = new int[4];\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {\n tmp[0] = input[4 * i] & 0xff;\n tmp[1] = input[1 + 4 * i] & 0xff;\n tmp[2] = input[2 + 4 * i] & 0xff;\n tmp[3] = input[3 + 4 * i] & 0xff;\n x[i] = tmp[0] << 24 | tmp[1] << 16 | tmp[2] << 8 | tmp[3];\n }\n // 进行32轮的加密变换操作\n for (int r = 0; r < 32; r += 4) {\n mid = x[1] ^ x[2] ^ x[3] ^ rk[r];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // x4\n x[0] = x[0] ^ l1(mid);\n mid = x[2] ^ x[3] ^ x[0] ^ rk[r + 1];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // x5\n x[1] = x[1] ^ l1(mid);\n mid = x[3] ^ x[0] ^ x[1] ^ rk[r + 2];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // x6\n x[2] = x[2] ^ l1(mid);\n mid = x[0] ^ x[1] ^ x[2] ^ rk[r + 3];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // x7\n x[3] = x[3] ^ l1(mid);\n }\n // 反序变换\n for (int j = 0; j < 16; j += 4) {\n output[j] = (byte) (x[3 - j / 4] >>> 24 & 0xFF);\n output[j + 1] = (byte) (x[3 - j / 4] >>> 16 & 0xFF);\n output[j + 2] = (byte) (x[3 - j / 4] >>> 8 & 0xFF);\n output[j + 3] = (byte) (x[3 - j / 4] & 0xFF);\n }\n }\n /**\n * @description: SMS4的密钥扩展算法\n * @param: key(加密密钥)\n * @param: rk(子密钥)\n * @param: cryptFlag(加解密标志)\n * @return: void\n */\n private void sms4KeyExt(byte[] key, int[] rk, int cryptFlag) {\n int r, mid;\n int[] x = new int[4];\n int[] tmp = new int[4];\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {\n // 实现对初始密钥的分组(分为4组)\n tmp[0] = key[4 * i] & 0xFF;\n tmp[1] = key[1 + 4 * i] & 0xff;\n tmp[2] = key[2 + 4 * i] & 0xff;\n tmp[3] = key[3 + 4 * i] & 0xff;\n x[i] = tmp[0] << 24 | tmp[1] << 16 | tmp[2] << 8 | tmp[3];\n x[i] = key[4 * i] << 24 | key[1 + 4 * i] << 16 | key[2 + 4 * i] << 8 | key[3 + 4 * i];\n }\n // 异或运算之后的结果\n x[0] ^= fk[0];\n x[1] ^= fk[1];\n x[2] ^= fk[2];\n x[3] ^= fk[3];\n for (r = 0; r < 32; r += 4) {\n //\n mid = x[1] ^ x[2] ^ x[3] ^ ck[r];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // rk0=K4\n rk[r] = x[0] ^= l2(mid);\n mid = x[2] ^ x[3] ^ x[0] ^ ck[r + 1];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // rk1=K5\n rk[r + 1] = x[1] ^= l2(mid);\n mid = x[3] ^ x[0] ^ x[1] ^ ck[r + 2];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // rk2=K6\n rk[r + 2] = x[2] ^= l2(mid);\n mid = x[0] ^ x[1] ^ x[2] ^ ck[r + 3];\n mid = byteSub(mid);\n // rk3=K7\n rk[r + 3] = x[3] ^= l2(mid);\n }\n // cryptFla==0 为解密,解密时轮密钥使用顺序:rk31,rk30,...,rk0(逆序)\n if (cryptFlag == DECRYPT) {\n for (r = 0; r < 16; r++) {\n mid = rk[r];\n rk[r] = rk[31 - r];\n rk[31 - r] = mid;\n }\n }\n }\n /**\n * @description: 加解密的基础方法\n * @param: in(待输入的明文或密文)\n * @param: inLen(16)\n * @param: key(密钥)\n * @param: out(待输出的密文或明文)\n * @param: cryptFlag(加解密的判断条件)\n * @return: int\n */\n private void sms4(byte[] in, int inLen, byte[] key, byte[] out, int cryptFlag) {\n int point = 0;\n int[] roundKey = new int[ROUND];\n sms4KeyExt(key, roundKey, cryptFlag);\n byte[] input;\n byte[] output = new byte[16];\n while (inLen >= BLOCK) {\n input = Arrays.copyOfRange(in, point, point + 16);\n sms4Crypt(input, output, roundKey);\n System.arraycopy(output, 0, out, point, BLOCK);\n inLen -= BLOCK;\n point += BLOCK;\n }\n }\n /**\n * @description: 明文加密\n * @param: plaintext(明文)\n * @param: key(密钥)\n * @return: byte[]\n */\n private static byte[] encodeSMS4(String plaintext, byte[] key) {\n if (plaintext == null || "".equals(plaintext)) {\n return null;\n }\n for (int i = plaintext.getBytes().length % 16; i < 16; i++) {\n plaintext += '\\0';\n }\n return Sms4.encodeSMS4(plaintext.getBytes(), key);\n }\n /**\n * @description: 不限明文长度的SMS4加密\n * @param: plainText(明文)\n * @param: key(密钥)\n * @return: byte类型的明文加密结果\n */\n private static byte[] encodeSMS4(byte[] plainText, byte[] key) {\n byte[] ciphertext = new byte[plainText.length];\n int k = 0;\n int plainLen = plainText.length;\n while (k + 16 <= plainLen) {\n byte[] cellPlain = new byte[16];\n for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {\n cellPlain[i] = plainText[k + i];\n }\n byte[] cellCipher = encode16(cellPlain, key);\n for (int i = 0; i < cellCipher.length; i++) {\n ciphertext[k + i] = cellCipher[i];\n }\n k += 16;\n }\n return ciphertext;\n }\n /**\n * @description: 不限密文长度的SMS4解密,获得byte类型的明文\n * @param: cipherText(密文)\n * @param: key(密钥)\n * @return: byte[]\n */\n private static byte[] decodeSMS4(byte[] cipherText, byte[] key) {\n byte[] plaintext = new byte[cipherText.length];\n int k = 0;\n int cipherLen = cipherText.length;\n while (k + 16 <= cipherLen) {\n byte[] cellCipher = new byte[16];\n for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {\n cellCipher[i] = cipherText[k + i];\n }\n byte[] cellPlain = decode16(cellCipher, key);\n for (int i = 0; i < cellPlain.length; i++) {\n plaintext[k + i] = cellPlain[i];\n }\n k += 16;\n }\n return plaintext;\n }\n /**\n * @description: 解密,获得明文字符串\n * @param: cipherText(密文)\n * @param: key(密钥)\n * @return: java.lang.String\n */\n private static String decodeSMS4toString(byte[] cipherText, byte[] key) {\n byte[] plaintext = new byte[cipherText.length];\n plaintext = decodeSMS4(cipherText, key);\n return new String(plaintext);\n }\n /**\n * @description: 16位明文加密,得到密文\n * @param: plainText(明文)\n * @param: key(密钥)\n * @return: byte[]\n */\n private static byte[] encode16(byte[] plainText, byte[] key) {\n byte[] cipher = new byte[16];\n Sms4 sm4 = new Sms4();\n sm4.sms4(plainText, 16, key, cipher, ENCRYPT);\n return cipher;\n }\n /**\n * @description: 解密密文,返回字节类型的明文\n * @param: key\n * @return: byte[]\n */\n private static byte[] decode16(byte[] ciphertext, byte[] key) {\n byte[] plain = new byte[16];\n Sms4 sm4 = new Sms4();\n sm4.sms4(ciphertext, 16, key, plain, DECRYPT);\n return plain;\n }\n /**\n * @description: 将16进制byte类型的密文转换为String字符串\n * @param: byteArray\n * @return: java.lang.String\n */\n private static String toHexString(byte[] byteArray) {\n if (byteArray == null || byteArray.length < 1) {\n throw new IllegalArgumentException("this byteArray must not be null or empty");\n }\n final StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();\n for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {\n if ((byteArray[i] & 0xff) < 0x10) {\n hexString.append("0");\n }\n hexString.append(Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));\n }\n return hexString.toString().toLowerCase();\n }\n public static void main(String[] args) {\n // 密钥\n byte[] key = {0x01, 0x23, 0x45, 0x67, (byte) 0x89, (byte) 0xab,\n (byte) 0xcd, (byte) 0xef, (byte) 0xfe, (byte) 0xdc,\n (byte) 0xba, (byte) 0x98, 0x76, 0x54, 0x32, 0x10};\n// byte[] key = "JeF8U9wHFOMfs2S3".getBytes();\n // 明文\n String plainText = "SMS4测试,大数据实战演练!";\n byte[] enOut = encodeSMS4(plainText, key);\n if (enOut == null) {\n return;\n }\n System.out.println("加密结果:");\n System.out.println(toHexString(enOut));\n byte[] deOut = decodeSMS4(enOut, key);\n System.out.println("\\n解密结果(return byte[]):");\n System.out.println(Arrays.toString(deOut));\n String deOutStr = decodeSMS4toString(enOut, key);\n System.out.println("\\n解密结果(return String):\\n" + deOutStr);\n }\n}\n\n
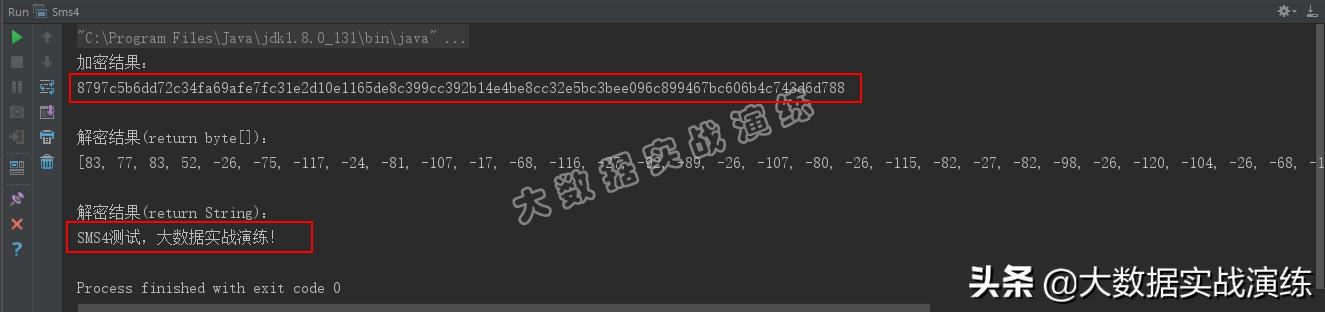
明文设置为“SMS4测试,大数据实战演练!”,程序会对明文进行加密,然后在对密文进行解密。直接运行程序,得到加密与解密结果,如下图所示:
不要忘记了,SMS4更多详细的资料请私信 “sms4” 到本头条号,获取相关资料(一个PPT,一个PDF)。
版权声明:CosMeDna所有作品(图文、音视频)均由用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流。若您的权利被侵害,请联系删除!
本文链接://www.cosmedna.com/article/678893965.html